Who needs to comply with the new rules?
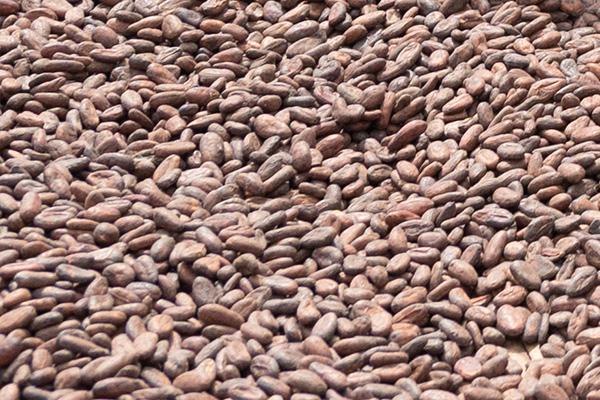

The new rules apply if you plan to place cocoa or any of the following products on the EU market, or to export them from the EU:
- Cocoa beans, whole or broken, raw or roasted
- Cocoa shells, husks, skins and other cocoa waste
- Cocoa paste, whether or not defatted
- Cocoa butter, fat and oil
- Cocoa powder, not containing added sugar or other sweetening matter
- Chocolate and other food preparations containing cocoa
How to comply with the new rules?
The products
- must be deforestation-free, meaning they come from a plot of land that was not deforested after 31 December 2020
- must have been produced in line with the relevant legislation in the country of production
- must be covered by a due diligence statement
Due diligence: 3 steps to follow

1. Collect information
Collect information, documents and data showing that the product is deforestation-free and legal, such as geolocation coordinates, quantity, country of production, etc
2. Risk assessment
Assess whether there is a risk the product does not comply with the rules

3. Risk mitigation
Adopt risk mitigation procedures and measures if there is a significant risk the product does not comply with the rules
- must be completed and submitted electronically in the new Information System
- will then be checked for compliance with the regulation
The new Information System is undergoing a Pilot testing. The Commission is working closely with Member State authorities to ensure that the System is fully functional before the new rules enter into application on 30 December 2024.
More information on Due Diligence including, including how to comply with the three steps mentioned above.
What actions need to be taken at each stage of the supply chain?
Cocoa must be produced legally and be deforestation-free. The producer must collect geolocation data of the area of production.
Cocoa that was produced illegally, or on land deforested after 31 December 2020, or Cocoa that is not traceable, does not comply with the rules. Compliant and non-compliant cocoa must be stored seperately.
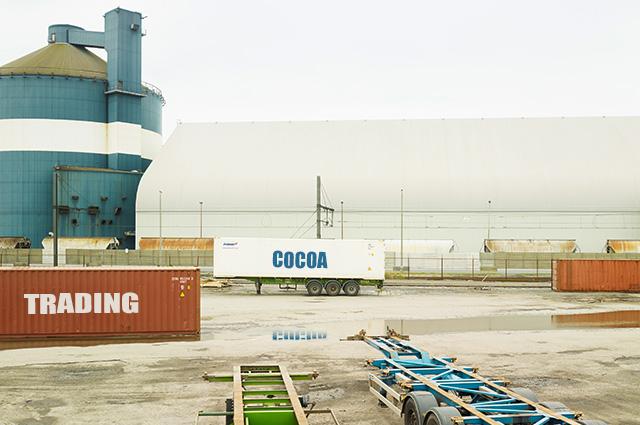

Deforestation-free and legal cocoa beans must be kept separate from other cocoa beans while being traded and shipped. Mixing compliant and non-compliant commodities, or commodities of unknown origin, is not allowed. In such cases, the whole shipment would be non-compliant and cannot be placed on the EU market.
The use of mass balance and mixed materials within the chain of custody model is not allowed.
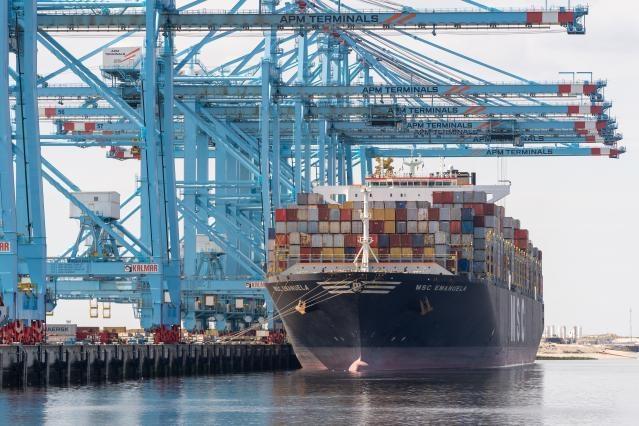

Before placing a product on the EU market, the importer must perform due diligence.
The importer submits a Due Diligence Statement and receives a reference number (and security token) which must be reported in the customs declaration for import.
Only compliant products may be placed on the EU market. The operator may place the cocoa on the EU market when it has been released for import by the customs authorities.

Large manufacturers of cocoa in the EU factories (for example producing chocolate) must perform due diligence.
Large manufacturers must check the Due Diligence Statement (DDS) of the importer, and submit their own DDS for their products, using the reference number of the upstream DDS. The operator then receives new DDS reference number and security token.

Before selling the cocoa product on the EU market or exporting it outside the EU, large companies must perform due diligence.
Large companies must check the Due Diligence Statements (DDS) made throughout the supply chain, and submit their own DDS, based on all previous reference numbers. The operator then receives a new DDS reference number and security token.
Small companies (SMEs) do not need to check nor submit due diligence statements.
The Sustainable Cocoa Initiative, launched in 2020, supplements the EU Deforestation Regulation by sharing its objective of tackling deforestation and by addressing technical issues for instance linked to traceability.
